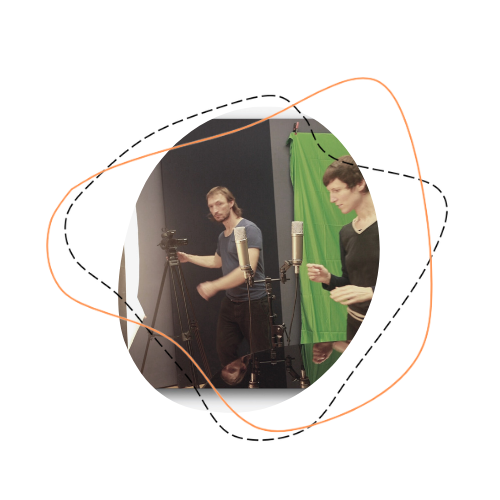
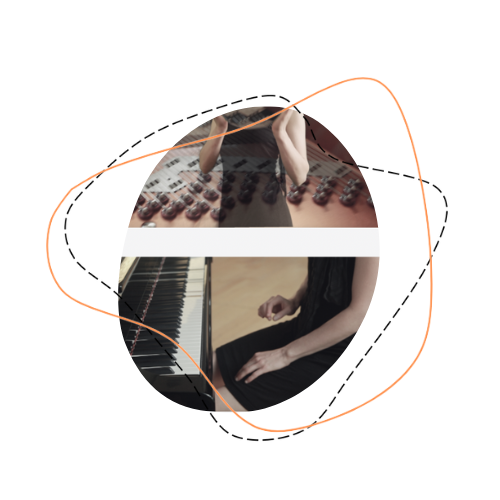
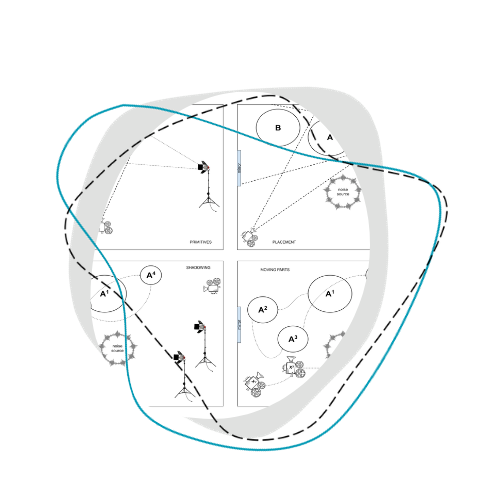
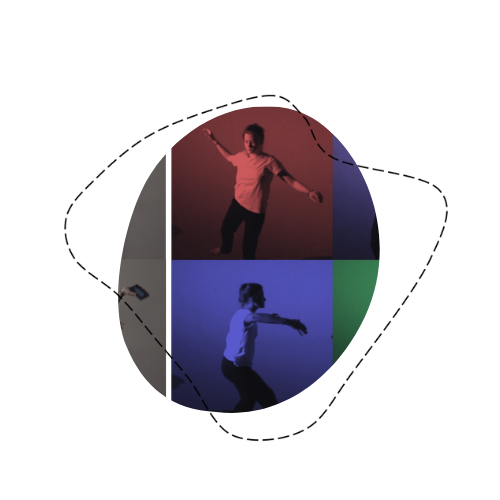
In order to organise our work around specific research problems / experimental setups, we found it useful to set up different labs. Each lab involves a different subset of researchers, and therefore approaches the project’s research questions from a different perspective.
Fractal Lab
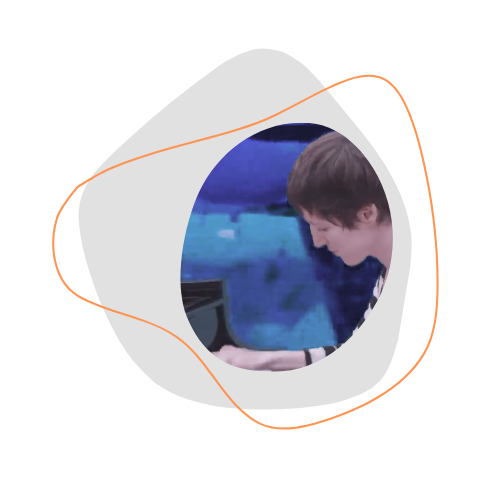
The Fractal Lab is rooted in the idea of an illusion of “fractal spatial qualities” created by sound oscillations, which are created by decomposing and phase-shifting musical motifs. From simpler studies for piano and recording device with compositions by Émile Jaques-Dalcroze and Klement Slavicky, a case study developed with the self-playing piano system CEUS by Bösendorfer. The study series was structured around six brief case studies. These investigated the concept of spatiality in its different facets and lead into a cycle of short pieces titled ‘six memos for a pianist and a self-playing piano’ after Italo Calvino’s unfinished lecture series ‘Six memos for the new Millenium’.
Here is some of the output produced in this Lab:
Furthermore in order to pursue this artistic investigation, we also developed a library of MaxForLive devices (TesserAkt) that perform all sorts of operations in the midi realm. These modules can be stuck in any configuration and connect to one another using midi CC messages. This library is open source and freely available for other artist-researchers to use and expand on:
Lab participants
Description Lab – Dialectic Attempts of A Eurhythmician And A Complexity Scientist
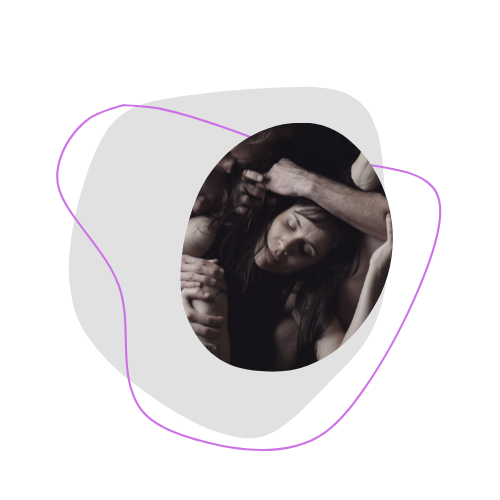
The Description Lab took place in the context of the null space research in the dicsipline of eurhythmics. The praxeological research material has been published in the form of an article in Le Rythme 2023, the annual journal of fier, and in an online exhibition
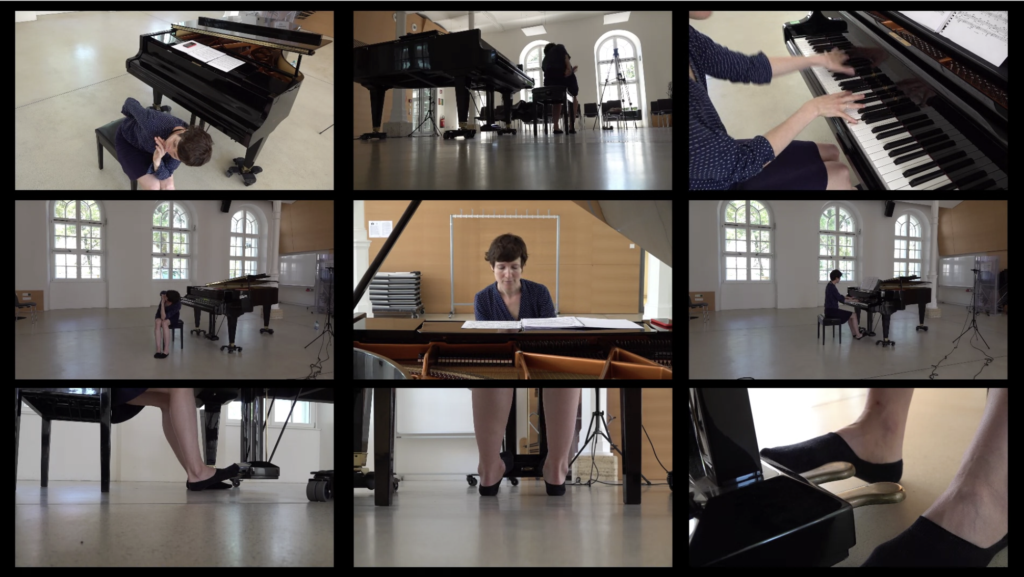


Here is some of the output produced in this Lab:
Lab participants
Desire Machine Lab
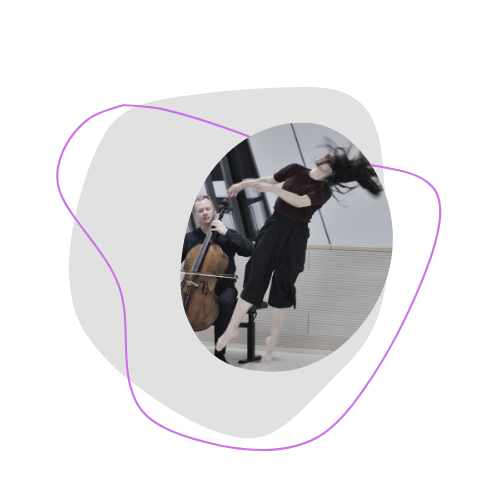
The Atlas of Smooth Spaces is concerned with the space that is created around performers, shaped through performers and accessed by performers. Following this approach Desire Machine is a proposition of a smooth performative space for movement, sound, and light. The elements are arranged through the logic of assemblage developed by Deleuze and Guattari in A Thousand Plateaus.
Among the key methodological questions of the PEEK project is the issue of capture and creation of the smooth spaces by the means of notation:
“We argue along the lines of Deleuze and Guattari, that capture and creation are related to each other via a duality, which is notation. A notation attempts to capture anything ephemeral, to fix a system out of the many possible ones. A notation confines. However within the confines and limitations of an alphabet, the playful and the intensive (related to intensivity/uncountability) can prosper. Thus notation is itself a form of striation, but at the same time both a method for capture and a method for creation of smooth spaces. This duality is explored in great detail in the work of Deleuze and Guattari: “It does not just go from the smooth to the striated, it reconstitutes smooth space, […] it reimparts smooth in the wake of the striated”. Therefore “it is possible to live smooth even in the cities, to be an urban nomad”. (Deleuze, Guattari 1987, p.482)
Desire Machine follows this proposition by creating an organizational structure that allows unity through multiplicity, the simultaneous capture – creation process. This is achieved through the application of technology as both a smooth and striated form of notation.
- Theoretical challenges – Desire Machines – The logic of Assemblage
For Deleuze and Guattari, desire is not to be identified with lack, with the law, or with the signifier, but rather with production, with desiring-production in the social field. For them, the Oedipal myth and its institutionalization in psychoanalysis stand directly in the way of understanding the productive unconscious.
Desiring machines are the site of that production. For Deleuze and Guattari, every machine is a machine connected to another machine. Every machine functions as a break in the flow in relation to the machine to which it is connected, but is at the same time also a flow itself, or the production of a flow.
The concept first appears in Anti-Oedipus (1977), but in A Thousand Plateaus (1987), they instead speak of abstract machines and assemblages, At the same time they retain the core idea that desire’s basic function is to assemble and render machinic.
Moving beyond the notion of structure—assemblage operates as a relay concept, “linking the problematic of structure with that of change and far-from-equilibrium systems” (Venn 2006, 107 as cited in de Assis, P., & Giudici, P., 2021).
With its interplay between organization and unpredictability, the assemblage works as a dynamic concept, linking the problematic of structure with that of chance and continuous change.
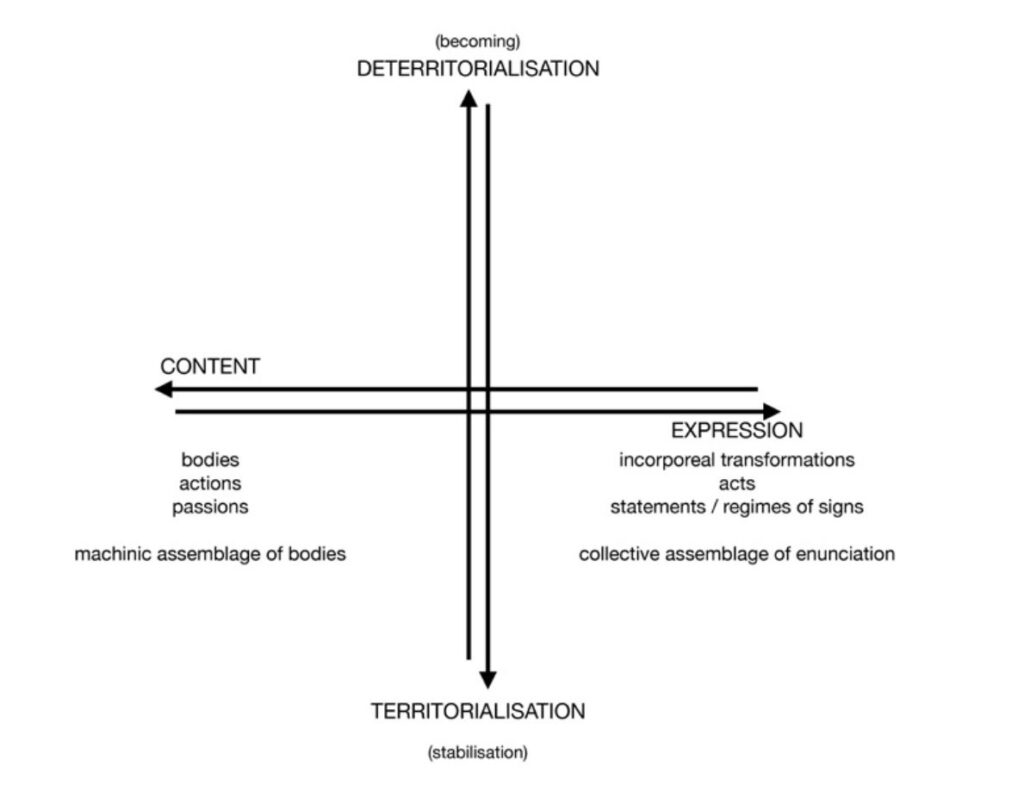
A logic of assemblage, imperceptibly moving between the poles of content and expression has several consequences: the overcoming of unity in favor of multiplicity, of the essence in favor of the event, of being in favor of becoming, of elusive certainty in favor of informed inconsistency.
Elisabeth Grosz in Volatile Bodies (1994):
“Subject and object are series of flows, energies, movements, strata, segments, organs, and intensities – fragments capable of being linked together or severed in potentially infinite ways other than those which congeal them into identities.
[…] Production consists of those processes which create linkages between fragments, fragments of bodies, and fragments of objects.
[…] It is not that the world is without strata, totally flattened; rather, the hierarchies are not the result of substances and their nature and value but of modes of organization of separate substances. They are composed of lines, of movements, speeds, and intensities, rather than of things and their relations. Assemblages or multiplicities, then, because they are essentially in movement, in action, are always made, not found. They are consequences of a practice…”
Anne Sauvagnargues in Artmachines (2016):
[…] both image and sign are considered as instances of real production […] only in the relation to other signs and images, situated in ‘rhizomes’ and ‘ecologies’ that should be approached through ethology and experimentation rather than through interpretation.
[…] We now think of images as individuations embedded in an ecology of images, always in a state of becoming.
Desire Machine Lab focuses on creating a map of the fragments of an Assemblage in:
* anti-Oedipus, non-representational way
* non-hierarchic way
* in a non arborescent, rhizomatic way
* between the lines of content and expression
* between the image and sign
* between experimental and poetic
References:
de Assis, P., & Giudici, P. (Eds.). (2021). Machinic Assemblages of Desire: Deleuze and Artistic Research 3. Leuven University Press. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctv1595mb9
Grosz, E. (1995). Volatile bodies: toward a corporeal feminism. Choice Reviews Online. https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.32-3246
Sauvagnargues, A., Verderber, S., & Holland, E. W. (2016). Artmachines: Deleuze, Guattari, Simondon. Edinburgh University Press. http://www.jstor.org/stable/10.3366/j.ctt1bh2jvt
Here is some of the output produced in this Lab:
Furthermore in order to pursue this artistic investigation, we also developed a library of MaxForLive devices (DesireMachine) that interface with the DMX lights system This library is open source and freely available for other artist-researchers to use and expand on:
Lab participants
Boom Lab
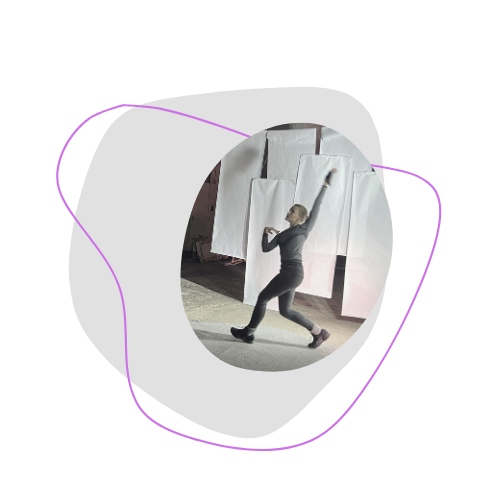
The Boom Lab is a case study in the context of null space research in the discipline of direct sound. Various research processes with the participation of experts from Vienna (Film Academy, Academy of Fine Arts), Berlin (Deutsche Film– und Fernsehakademie Berlin, DFFB and Universität der Künste, UdK) and Potsdam (Filmuniversität Babelsberg Konrad Wolf) followed an experimental and recursive workflow.
Here is some of the output produced in this Lab:
Furthermore in order to pursue this artistic investigation, we also developed a MaxForLive device (SmoothOperator) that eavaluates smoothness in body movement in real time. This repository is open source and freely available for other artist-researchers to use and expand on:
Lab participants
Choir Lab
In the Choir Lab we discussed the underlying spatial concepts of choral scores from different epochs. The starting point of our discussion was Ligeti’s Lux Aeterna, which we worked on in the context of the participative performance Conducting Spaces at the Ars Electronica Festival in September 2021. The perfomance was directed by Hanne Pilgrim, Johannes Hiemetsberger with “company of music” and Adrian Artacho. This was our departure point for investigations into gestural notations and the emergent spatial effects of Ligetis piece. In the Lux Aeterna score we considered discrete time units to create intensive spatial qualities. We organized a special Lux-Aeterna workshop on the 15th of October 2021 to discuss experimental setups. The next smooth space lab focused on a particular setup, where a group of 16 participants was involved. We explored the 16 voices of the Lux Aeterna piece by a gestural movement improvisation, and captured the respective movements with a MiMU glove using Ableton Live. We also included video capture.

For more details see “Lux Aeterna Lab”….
Here is some of the output produced in this Lab:
Lab participants
Gesture Lab
The Gesture Lab is specific attempt to generate a notation from choreomusical gestures. Within the scope of this lab is the implementation of certain quantitative methods, that can be applied to the research of human gestures in a performative context.
Here is some of the output produced in this Lab:
Lab participants
Movement Choir Lab
In the Movement Choir Lab we compared, discussed and studied different choral scores that contain movement or scenic elements (see reference list below). Among other things, these discussions also served to look at how the different disciplines of choral conducting, eurhythmics and dance are related to each other in these scores.
Scores:
- Jaques-Dalcroze, Émile (EJD) (1915). Nouvelles Chansons avec gestes op.60. Lausanne: Jobin et Cie.
- Orff, Carl: Tanzlieder aus dem “Orff-Schulwerk” / Carl Orff, Gunild Keetman (1950–1954): Musik für Kinder. Bände 1–5. Schott Musik International.